Introduction to Vacuum Forming
What is Vacuum Forming?
Vacuum forming is a simplified version of thermoforming, where a sheet of plastic is heated to a forming temperature, stretched onto a single-surface mildew, and pressured towards the mould via a vacuum. This method has been round because the 1930s and is especially famous for its fee-effectiveness and flexibility.
Brief History of the Process
The vacuum forming process was first developed in the 1930s as a method to make simple plastic products. Over the decades, it has evolved with advancements in materials and technology, making it a popular choice for various applications.
Comparison with Other Forming Techniques
Unlike injection moulding, which is better for high-volume production, vacuum forming is more cost-effective for small to medium batch sizes. It also allows for quicker prototype development compared to other methods like CNC machining.
Components of a Vacuum Forming Machine
Overview of the Machine Setup
A typical vacuum forming machine includes a frame, heater, and a vacuum source, all designed to manipulate plastic sheets into desired shapes.

Key Components and Their Functions
- Frame: Holds the plastic sheet in its place so that it cannot move.
- Heater: Softens the plastic to make it malleable.
- Vacuum Source: Removes air to form the plastic against the mould.
Types of Machines Used in the Industry
There are various types of vacuums forming machines, ranging from simple manual setups for small-scale operations to sophisticated automated systems for industrial use.
Materials Used in Vacuum Forming
Commonly Used Plastics and Their Properties
Materials like Acrylic, PETG, and PVC are commonly used due to their flexibility, durability, and aesthetic qualities.
Selection Criteria for Materials
The choice of material depends on the product requirements such as clarity, strength, and heat resistance.
Environmental Considerations and Recycling
Plastic selection is also influenced by environmental considerations. Many companies are now opting for recyclable or biodegradable plastics to minimize environmental impact.
The Vacuum Forming Process
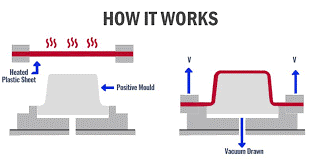
Step-by-Step Process Overview
- Preparing the Plastic Sheet: The plastic sheet is clamped into the frame.
- Heating the Plastic to Formability: The sheet is heated until it becomes soft and pliable.
- Applying Vacuum to Shape the Plastic: Vacuum is applied, sucking the plastic sheet against the mould to form the shape.
Mould Design and Construction
Types of Molds (Male vs. Female)
Male moulds are convex, while female moulds are concave, affecting the final product's detail and depth.
Materials Used for Molds
Materials range from inexpensive wood and plastics for prototypes to metals for long-term production.
Design Considerations for Optimal Results
Good mould design must account for proper draft angles, wall thickness, and undercuts.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Typical Problems Encountered During Forming
Common issues include webbing, poor detail, and trapped air.
Solutions and Preventive Measures
Adjustments in temperature, mould design, or vacuum pressure can resolve most issues.
Importance of Maintenance and Calibration
Regular maintenance ensures consistent quality and prolongs the machine's life.
Applications of Vacuum Forming
Industries That Benefit
- Automotive: Components like dashboards and door panels.
- Packaging: Product packaging and trays.
- Consumer Products: Everything from toys to appliance housings.
Innovative Uses of Vacuum Forming
- Medical Devices: Sterile enclosures and equipment housings.
- Architectural Models: To create the facades of building in their models.
- Custom Product Enclosures: Tailored housings for various electronic devices.
Case Studies
Real-world examples include packaging for consumer electronics where vacuum forming has provided both protection and aesthetic appeal.
Advancements and Innovations in Vacuum Forming
Technological Enhancements
Recent innovations include automation in the vacuum forming process and the use of advanced materials with improved performance characteristics.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Efforts are being made to reduce waste and energy consumption in vacuum forming processes, with a shift towards using recycled and biodegradable materials.
Future of Vacuum Forming
The future looks promising with advancements in materials and technology, expanding the possibilities of vacuum forming applications.
Best Practices and Expert Tips
Design Tips for Vacuum Forming
Optimizing design for manufacturability involves considering factors like draft angles and wall thickness from the early stages.
Selecting the Right Machine and Materials
Choosing the right machine and materials can significantly affect the efficiency and quality of the final product.
Maintaining Equipment for Longevity
Routine maintenance and timely replacement of worn-out parts are crucial for the longevity of vacuum forming machines.
Conclusion
Summary of Key Points
Vacuum forming is a versatile and cost-effective method suitable for a wide range of applications, from industrial components to consumer products.
Future Outlook
As we continue to innovate and improve materials and processes, vacuum forming remains a vital technique in the manufacturing landscape.
FAQs
- What is the most cost-effective material for vacuum forming?
- How does vacuum forming compare to injection moulding in terms of cost and efficiency?
- Can vacuum forming be used for high-volume production?
- What are the limitations of vacuum forming?
- How can one ensure the quality of a vacuum-formed product?
Find us
Factory
Shed no. 2, 3 & 4, Survey no. 25/2 & 25/3
New no. 391, Hosur Main Road, Chandapura
Bangalore - 560099
INDIA
HQ
Maini Group, Maini Sadan
No. 38, 7th Cross, Lavelle Road
Bangalore - 560001
INDIA
Let's Talk
-
Abishek Manimaran
-
Jishnu Nambiar (Kerala & TN)
-
Vijetha Varma
-
Pratheek U Shetty
©
. Maini Plastics & Composites Pvt. Ltd. All rights reserved.
Powered by Technoworth
Maini Plastics & Composites Pvt. Ltd.
Factory
Shed no. 2, 3 & 4, Survey no. 25/2 & 25/3
New no. 391, Hosur Main Road, Chandapura
Bangalore - 560099
INDIA
HQ
Maini Group, Maini Sadan
No. 38, 7th Cross, Lavelle Road
Bangalore - 560001
INDIA
Let's Talk
-
Jishnu Nambiar (Kerala & TN)
-
+91-895-194-3688
-
Vijetha Varma
-
+91-998-028-1023
-
Pratheek U Shetty
-
+91-990-054-1607
+91-990-007-5846
-
Abishek Manimaran
-
+91-890-406-2149
©
. Maini Plastics & Composites Pvt. Ltd. All rights reserved.
Powered by Technoworth